Why ROS?
ROS adds value to most robotics projects and applications, but the question remains “Does it add value to my use case?” The answer to the question can be difficult, but hopefully you can answer that for yourself after we introduce you to the features in ROS and show you some testimonials from people who have used ROS and come from many different robotics domains. First we will cover some of the reasons you might want to consider using ROS.
A Distributed, Modular Design
ROS was designed to be as distributed and modular as possible, so that users could use as much or little of ROS as they desired. We’ll cover what components make up ROS in the Features of ROS page, but the modularity of ROS allows you to pick and choose which parts are useful for you and what parts you’d rather implement yourself.
The distributed nature of ROS also fosters a large community of user contributed packages which add a lot of value on top of the core ROS system. At last count there were over 3,000 packages in the ROS ecosystem, and that is only the ROS packages which people have taken the time to make available to the public. These packages range in type, covering everything from proof of concept implementations of new algorithms to industrial quality drivers and capabilities. The ROS user community builds on top of a common set of infrastructure to provide an integration point which provides access to hardware drivers, generic robot capabilities, development tools, useful external libraries, and more.
A Vibrant Community
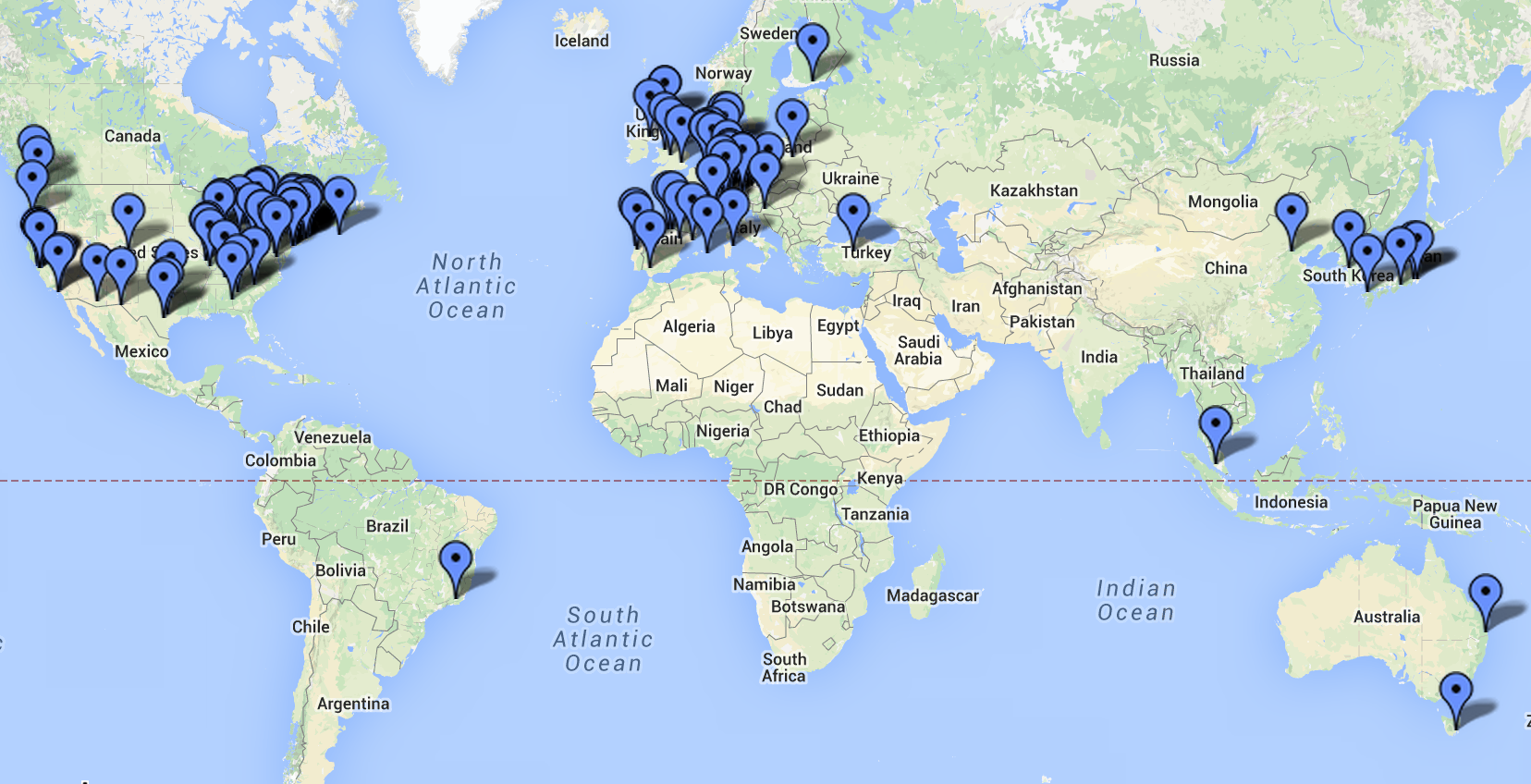
Over the past several years ROS has grown to include a large community of users world wide. The majority of the users are in the Academic domain, but increasingly we are seeing more and more users in the industrial and service robotic products domain.
The ROS community is very active. According to our Metrics, the ROS community has over 1,500 participants in the ros-users mailing list, more than 3,300 users on the collaborative wiki.ros.org documentation wiki, and some 5,700 users on the community driven answers.ros.org Q&A website. The wiki has more than 22,000 wiki pages and over 30 wiki page edits per day. The Q&A website has 13,000 questions asked to date, and a 70% percent answer rate.
Permissive Licensing
The core of ROS is licensed under the standard three-clause BSD license. This is a very permissive open license which allows for reuse in commercial and closed source products. You can find more about the BSD license here:
While the core parts of ROS are licensed under the BSD license, other licenses are commonly used in the community packages, such as the Apache 2.0 license, the GPL license, the MIT license, and even proprietary licenses. Each package in the ROS ecosystem is required to specify a license, so that it is easy for you to quickly identify if a package will meet your licensing needs.
A Collaborative Environment
ROS by itself offers a lot of value to most robotics projects, but it is also an opportunity to network and collaborate with the world class roboticists who are also in the ROS community. One of the core philosophies in ROS is shared development of common components. If you find some part of ROS useful we encourage you give back and help maintain or improve parts of ROS which need attention, though obviously it is not required.